The first in a series of articles on Ontology’s contribution to the coming Web 3.0 era.

From how we communicate with one another, to how we work, to how we consume entertainment and acquire knowledge, the internet has pervaded practically every aspect of our lives. The internet’s rise has coincided with a corresponding rise in the influence of what has become known as “Big Tech”, a collection of technology companies responsible for the online platforms and services we use on a daily basis. These companies created platforms that attracted millions (in some cases, billions) of users. In order to use such platforms, users are required to provide information in the form of email addresses, phone numbers, etc. The tech companies discovered that they could monetize these data points by using them to create targeted advertisements and also by selling them to third-parties.
The current Web 2.0 world has come to represent the era of “Big Data”, a world in which users provide private data to centralized tech platforms that utilize the data to enrich themselves. In essence, these “free” platforms have transformed their users into a kind of product. You, the user, have very little (if any) control over how your data is utilized once it is shared with a given tech platform. And since it is stored on a centralized platform, it is prone to hacking. Numerous data breaches have occurred in recent years, exposing the private information of millions of users.
We are currently in a transition phase between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0. The Web 3.0 era promises a world in which we are no longer at the mercy of centralized platforms. It is a decentralized world; one that will allow people to reclaim ownership and control over their private data.
What is Web 3.0?
There are different opinions on what Web 3.0 is with no clear definition. The “Semantic Web”, “Global Brain”, and “IoE” proposed by Tim Berners-Lee still seems out of reach. According to Deloitte’s 2019 report on The Spatial Web, compared with Web 2.0, the era of Web 3.0 will undergo qualitative changes at three levels: interaction, computation, and information.
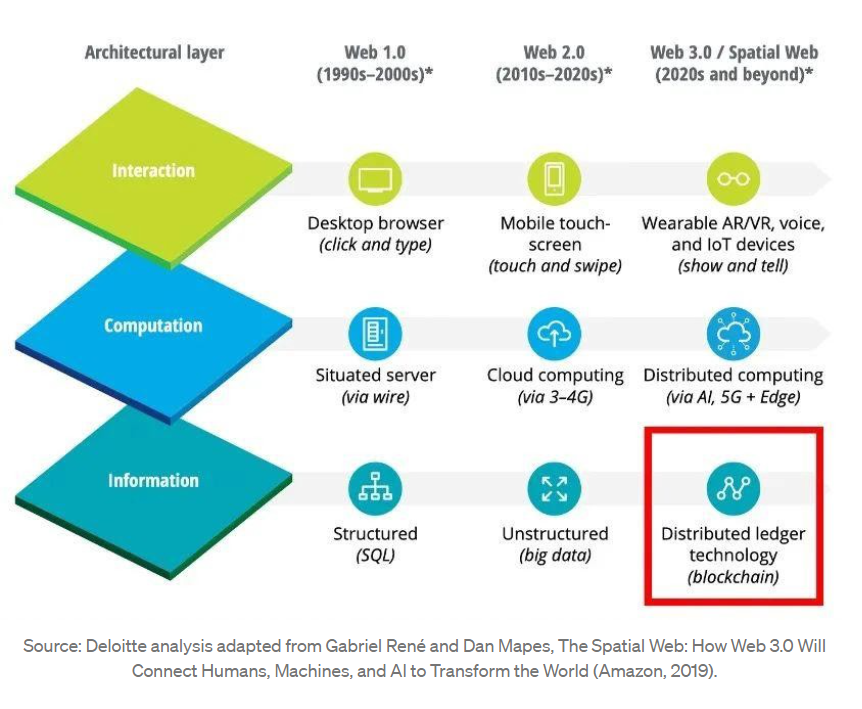
According to Forbes, the rise of technologies such as distributed ledgers and storage on blockchain will allow for data decentralization and create a transparent and secure environment. This helps to address the centralized Internet quandary described above. When users are able to control their data (and decide who can access it) independently, centralized platforms will be unable to covertly harvest private data. In addition to improving privacy, this should also help prevent data breaches, as the data will no longer be stored on centralized servers. In sum, Web 3.0 puts the power back in the hands of users, bidding farewell to the data hegemony and data exploitation of the centralized platforms.
Ontology, a blockchain for self-sovereign identity and data, is helping bring about the Web 3.0 era. Thanks to Ontology’s decentralized identity framework, ONT ID, netizens no longer need to place their trust in centralized platforms. If a person needs to verify aspects of his identity online, he can do so knowing that his data remains private and secure. Right now, individuals unknowingly provide huge swaths of data to centralized platforms that store it on centralized servers. Ontology enables users to create a decentralized identity that they can carry with them and utilize across multiple platforms. Decentralized identity is a core pillar of the coming Web 3.0 infrastructure and Ontology is poised to provide the tools necessary to facilitate the transition away from Web 2.0, characterized by centralized data platforms, and towards the decentralized and open Web 3.0 era.
Web 3 and Ontology
Compared with the current Web 2.0 landscape characterized by centralized platforms that store and monetize user data, Web 3.0 represents a more open, transparent, and decentralized future. Blockchain has been an open and collaborative project from the very beginning. When Ethereum emerged, it was known for its neutrality, open source, and programmability, and thus became one of the largest and most active blockchain communities in the world. The blockchain industry still needs time to mature if it is to become a truly decentralized and interoperable network for Web 3.0.
In line with the openness of Web 3.0, Ontology was based on the concept of “multi-chain compliance, multi-layer expansion, and on-chain and off-chain hybrid application mode”, Ontology is an interoperable public chain supporting cross-chain transactions and Layer 2 solutions that enhance performance. It is also equipped to work with a variety of industries, both traditional and blockchain-based.
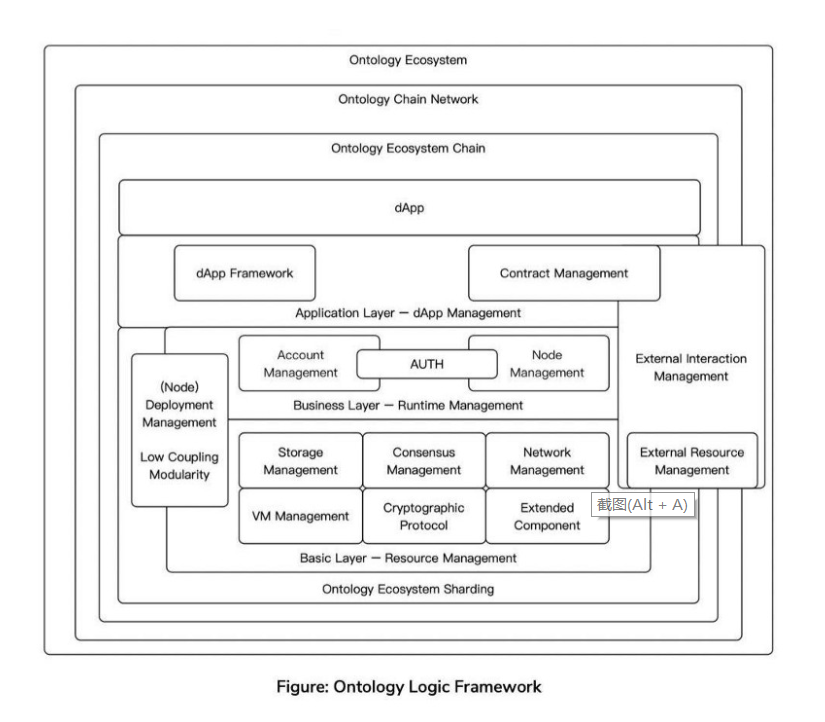
Ontology’s smart contract system utilizes a universal multi-virtual machine solution, being the first to support NeoVM, Native Ontology, and Wasm contracts in 2020. This year, Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) support was added, giving developers the widest variety of VM options currently available. After the EVM tests are completed, Ontology will become the first public chain to support four virtual machines.

As a highly interoperable chain network and the multi-virtual machine solution, Ontology is equipped for the coming transition to Web 3. Whether you are a senior blockchain developer or a traditional web developer, you can quickly become familiar with the Ontology development environment, easily deploy blockchain applications, and enjoy fast block confirmation speeds and low deployment costs. Ontology has matured into a comprehensive system with multifunctional, lightweight, highly available, concurrent, multi-language, cross-contract, cross-virtual machines all in one place and compatible with any region, any ecology, any language, and any business.
Our exploration of Ontology and Web 3.0 continues next week in Part 2 of this series.
References
1. Deloitte analysis — The Spatial Web: How Web 3.0 Will Connect Humans, Machines, and AI to Transform the World
https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/topics/digital-transformation/web-3-0-technologies-in-business.html
2. Forbes — What Is Web 3.0?
https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2020/01/06/what-is-web-3-0/?sh=70aa418758df
3. Ontology White Paper https://docs.ont.io
